
Introduction
on astronomy
Planet
systems - Solar systems
When
it comes to the question whether other solar system exists apart from ours,
Yes indeed.
There
are thousands of other proven solar systems beside ours - however all of
them are non-orbiting planets around the solar system. So we are talking
only about double- and multiple star systems- without orbiting planets.
And
no sun (star) exists in the planet systems.
Only
one sun with planets is proven in the entire well-known universe. No further
systems with sun (or suns) and planets have been
proven.
The
planets orbit only around our sun.
Those
planets have not been found out in which conscious life would
have been possible.
This
is practically unknown by the population, it is assumed that this is kept
as a secret. Planets have their orbit only around our sun. Every time we
talk about solar systems, we mean only star systems (or double solar systems)
without orbiting planets. See also solar
system

Double
sun Albireo
(photo:
Marcel Klein, VSW Hagen)
DOUBLE
SUN = double star
Here
circle two or several suns each other. To that extent the term "solar system"
is correct, however no planets are available, which draw their courses
around the central sun(s). So far, when only planets are available in the
system and no sun, then the term "planet system" is correct instead of
"solar system".
 One often
talks of "solar systems" in the literature, even if "planet systems" are
actually meant. Naturally, a sun is always located as central star in the
solar system.
One often
talks of "solar systems" in the literature, even if "planet systems" are
actually meant. Naturally, a sun is always located as central star in the
solar system.
The
term star is reserved for other suns in the astronomy.
It
is not used for planets. The white points at the starlit sky are suns,
thus stars which possess an own radiation strength. These are not planets.
http://www.astronomie.de/sonnensystem/index.htm
How
huge are the largest star in the universe?
Probably
several thousands times the diameter of our sun.
Beteigeuze
for example has about such a diameter.
Why
is the earth in daily rotation?
Nobody
knows exactly why. It is assumed that it still comes from the Big Bang.
The raw material was also to be found in rotation.
Are
there gravitation waves?
The
existence of gravitation waves follows from Einstein General Relativity
Theory. So far these were not proven yet. Gravitation waves cause a distortion
of the space.
When
are all planets in our solar system close to each other?
-
At next, the planets were formed on 11 April 1128 -
they were into a sector of only 40 degrees.
-
on 1st of February 949, they were into a sector with an angle of 80 degrees.
-
on 6th of May 2492, they will be in a sector of 90 degrees.
-
20.4.2002 to 4.5.2002 - The planets are located in conjunction:
Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. The earth (terra) is in opposition ( other
side of the sun). Approximately in 20 years it will give the same
constellation.
All
are visible with the naked eye. Naturally only at night with free view.
They
were never located in a line and will never be located; so this could the
end of the earth or the solar system. The equilibrium of the system would
be disturbed.
Fundamental
to the galaxy .
Our
galaxy - the Milky Way - consists of approximately 10 billion stars and
is a spiral galaxy. It has a diameter of approximately hundredthousand
of light years. Our sun is far away from the center of the galaxy
and orbits the center with 220km/s (almost 800,000 kilometers per hour)
on an almost circular course. The light of the center of the Milky Way
needs about 25000 years, in order to reach us. In comparison: the light
needs only about 8 minutes from the sun to reach the earth. Other galaxy
types are elliptical galaxies, S0-Galaxien, irregular (only from the outer
appearance) and dwarf galaxies. Galaxies mostly form groups or clusters.
These form anew superclusters, which are separated from each other from
huge empty spaces (voids).
The
Milky Way belongs to the local group, together with the Andromedanebula,
the M33-Galaxie, and as well as more than two dozen of dwarf galaxies.
The local group have an expansion of approximately 5 million light-years.
It is part of the Virgo supercluster. The Virgo galaxy cluster is at a
distance of aproximately 50 million light-years from us. It contains about
one hundred elliptical S0- and spiral - galaxies and over thousand
dwarf galaxies. The total number of the galaxies in the observable part
of the universe amounts to more than one trillion galaxies. The light,
which we receive from the furthest galaxies, was sent more than 12
billion years ago, thus only about 2.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
Tardoxx:
Gravitation
- attraction
To
understand one must make oneself clear that forces result only from the
presence of a mass (a planet or a star), which affect other masses.
Thus,
comet appear to us every 76 years. This appearance rhythmus stays due to
the gravitation attraction. The comet disappears then again in billions
of kilometers and appears then again in the proximity of the earth. Only
due to its mass, it is pulled from the sun. See glossary comet
Gravitation-Development
What
is a geodaete ?
Geodaete
with consideration of the gravitational pull
A Geodaete
is generally the shortest connection between 2 points on the earth's surface
- this is called: the great-circle.

Legend:
If we want to go on the earth's surface from the point A to the point B,
the shortest way would be in a straight line along the
yellow line through the earth. Since this
is not possible, we will obligatorily have to go on the
red line on the earth's surface . That would
be then under these circumstances the shortest way to the point B.
The
red way is the Geodaete (great - circle) and
longer than the yellow
way. We go however the red
way without noticing , that we are rerouted. In the case of airplanes,
the
red line is also the shortest way from A to
B.
SEE also Space Curvature
Beam
deflection
The
way of the light beam is curved within the area of a mass (s. picture down
beam
deflection ).
Why
are light beams also deflected from the attraction of planets, although
light does not possess any mass?
To
understand this procedure we imagine the following:
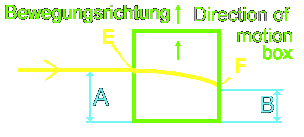
The
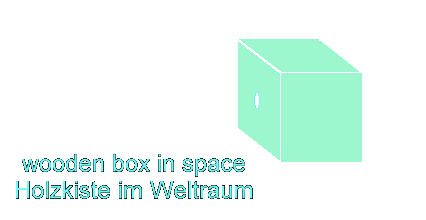
wooden box in space
A box
floats in weightless space in the proximity of a sun. The box contains
void of air - in other words - vacuum.
The
wooden box is now accelerated by a rocket with 9.81 meters for each second
square in the space. That is the same earth acceleration due to gravity,
which exists on earth. The box possess a small hole at the side panel,
into which sunlight breaks in.
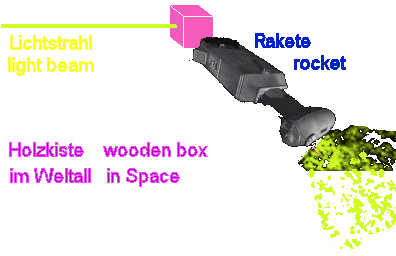
Diagram:
box in space is accelerated by rocket
The
beam penetrates into the box through the hole and hits on the other side
of the panel and withdraws again from the box.
However,
the box continues to moves on its own speed (pushed by the rocket) even
while the light flows from one side to the other side of the panel. Thus,
the light-beam changes its direction; it is the difference between measurements
"
A " and " B ". This difference depends on the speed and acceleration
of the box. That was the preface - now to 3 separated cases:
.
.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
_.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
Case
1:

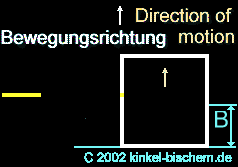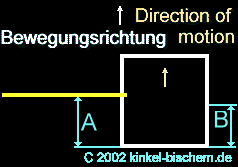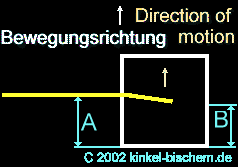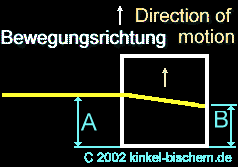
Situation:
The box is not accelerated by the rocket - the box is weightless in the
space. The light beam penetrates into the hole; the box does not move,
since no acceleration is available, therefore the light beam ist not shifted
in this case. The beam penetrates the hole into the box at point "E" and
reach point "F" on the opposite wall. Without acceleration by the rocket,
the measurement "A" and "B"
remains
the same and the beam in the box is a straight line.
.
.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
_.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
Case
2:
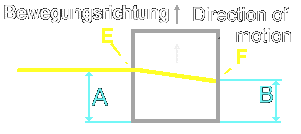
Case
2:
Situation:
The box is in the status after accelerated by the rocket and floats now
with regular speed there.
The
light beam penetrates into the hole, the box moves forward in regular speed
and the light beam reach the other side of the panel, shifted in its position
through the acceleration of the rocket. The beam penetrates the hole in
the box at point "E" and reaches point "F" un the opposite wall.
This
light curvature is for an observer only within the box noticeable, only
for those, who are subjected also to the acceleration of the rocket. For
an observer, who is found to be outside the box, the light curvature is
not available, since the beam flowes is a straight path.
The
invasion of the light beam is subjectively seen from the box, i.e. the
box is fixed steadily by the observer and the movement of the box is not
perceived.
The
box is admittedly still in motion, but the light beam remains on its previous
place and mores only in its direction.
Subjectively
seen from the light beam, it's still in motion in a straight line and does
not bend. The measurement of "A" is larger than the measurement of
"B". The light beam forms a straight line within the box.
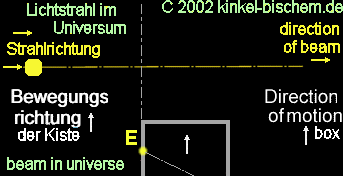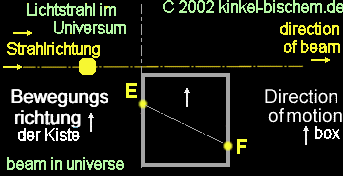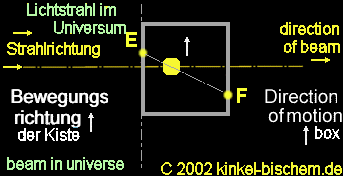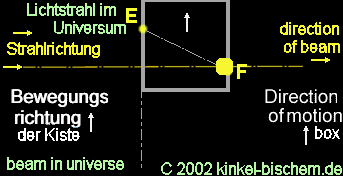
The
light beam in the diagram is fixed and the box moves firmly.
At
the point "E" , the light beam penetrates and hits the wall on the opposite
side at point "F". The beam has proceeded as usual an even course, however
not for the observer, who is found to be in the box.
.
.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
_.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
Case
3
Case
3:
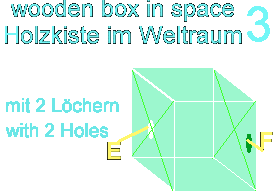
The wooden box
in space possesses two holes, one in the front ( here flows the beam in
the box) and back side (here, the beam withdraws from the box). The distance
of the holes can be determined from the rates of the box and the light.
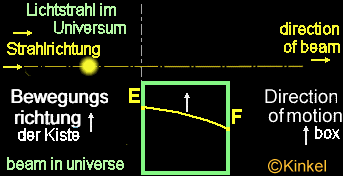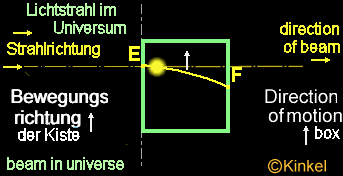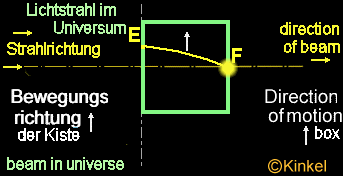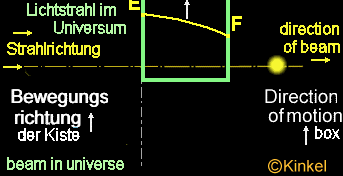
Situation:
The box is constantly further accelerated by the rocket and flies with
constantly increasing speed in the space. The light beam falls into the
hole. The box continues to moves on and the light reach the other side
of the panel, shifted from its position through the acceleration. The beam
penetrates the hole into the box at point "E" and reach the opposite side
at point "F".
The
beam leaves then the box. The box still moves on, but the light beam remains
on its previous course and moves only in its direction. Subjectively seen
from the light beam - this means that we are observing only the light beam.
Other way round, we would observe the box (see case 2).
Here
in the case 3, the beam make back a hyperbola - thus a curve. This is the
result of additional acceleration and the rising speed. The observer outside
of the box sees the light beam however moving further in a straight line
without changing its position.
For
the observer within the box is the measurement "A" larger than the measurement
"B". This light curvature is only for an observer within the box noticeably,
only for those, who are also subjected to the acceleration of the rocket.
For those, who are found to the outside the box, the light curvature is
not available, since the beam moves in a straight line.
The
cases 1 to 3 prove that the rays of light also appear curved without actual
bend. But there is also the other case that sunbeams experience a diverson
(bend) by the gravitation.
The aforementioned possibilities of the apparent beam
deflection
in geometrical form are present. This circumstances change
however nothing in the fact that rays of light are also
affected
by the force of gravity.
. .: * ~ *:. _.:
* ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.:
* ~ *:.
. .: * ~ *:.
_.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
_.: * ~ *:.
Light
beams at the sun
The
same applies to light which is found in the proximity of suns or planets.
Even this light beam remains in a straight line for observers outside the
box. One must imagine, according to the situation,
to be inside the box, since the curvature is only noticeable within the
box.
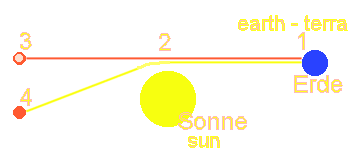
Diagram:
Beam deflection
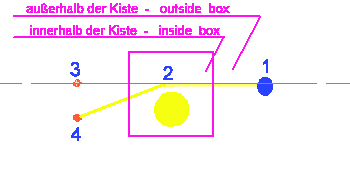
To
the diagram beam deflection:
In
the environment of massive heavenly bodies the space is curved by the gravitation
(attraction). That applies also to light beams. From the star at point
4, light beams are transmitted. The star is seen from the earth. However,
we mean that the star is located at point 3. But the beams turn at
point 2 and the star is
actually
located at point 4. All this is due to the curvature of the space.
The
shortest connection between 2 points in the curved space is the curve.
When comets move outside the solar system and are able to move back to
the sun , this applies to the characteristic , that comets are also found
to be on the shortest way (an elliptical course).
The
gravitation curves the space and the space moves the matter. Curvature
is actually defined as to bend a straight line to a curvature which means
to an ellipse. That is the shortest way around a sun in a curved space.
Planets also take elliptical course.
Course
curvatures

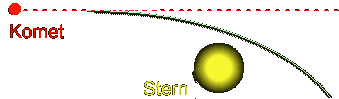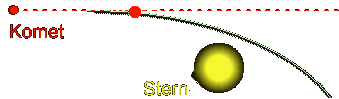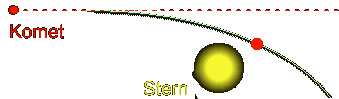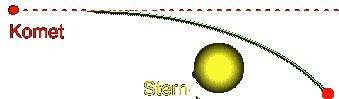
The
comet is diverted from its even course into a curve through the gravitation
attraction of the sun (red dashed)

Picture
of sun and the planets
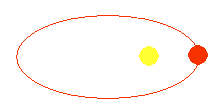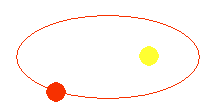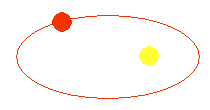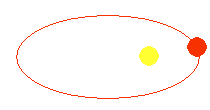
Earth in elliptical course
Summary - light-beam curvature (bend):
It happens in different
cases:
1) the light-beam curvature
(bend) occurs as in the examples with the "box in space". see
HERE
However in this case no
actual diffraction of ray of light is
present, but it only appears
like this for the observer in the crate. For an observer outside the box,
the ray of light move accurately straight on. HERE
2) A light-beam curvature
(bend) is caused by the gravitation.
Both are correct.
Background
information
see
light beam curvature and seeing
of human part 1 - part
2
How
is an object seen Entire
on curved space-time
Distances
earth - moon Erde – Sonne
8 Lichtminuten lightminutes lm
sun pluto
Sonne – Pluto
4 Lichtstunden = 0,0003 Lj lightyears
next star - nächster
Stern: Proxima Centauri 4,1 lj
Lichtjahre lightyears
centrum milky way Zentrum Milchstraße
30.000 Lj
next galaxy nächste Galaxie:
Magellansche Wolke 160.000 Lj
Andromeda-Galaxie
2.200.000 Lj
Zentrum Virgohaufen
50.000.000 Lj
next - nächster Quasar
500.000.000 Lj
farest object entferntestes
Objekt 14.000.000.000 Lj
kosmischer Horizont (3 K-Strahlung)
15.000.000.000 Lj
.
. .: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
_.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
Author:
Robert Kinkel on 2002.4.4 after Christ
Translation
- German to English: Tara Kinkel on 2003.7.7. after Christ
|