|
- small introduction 1 - small introduction 2 - - small introduction 3 - small introduction 4 - :*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:. KinkelCyclesTheory1 :*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:.
|
|
All part reports over Space-time curvature are summarized in one page
You
must be able to imagine with interllectual eyes that a ball bounds here
and there in a three-dimensional room. This is important for the understanding
of the curved space. Three-dimensional thinking is a prerequisite for this.
Just imagine the ball starts to fly and hit the wall.
..:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:._.:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:._.:*~*:..:*~*:.
Gravitation
- attraction
Thus, comet appear to us every 76 years which is held in the appearance rhythmus due to the gravitation attraction. The comet disappears then again in billions of kilometers and reappears again near the earth atmosphere. comet Gravitation Geodaete in consideration of the gravitational pull A Geodaete
is generally the shortest connection between 2 points on the earth's surface
- this is called: the great-circle.
Why are light beams also deflected from planets, although light does not possess mass? To understand this procedure we have to imagine the following: The wooden box in space A wooden
box floats in weightless space in the proximity of a sun. The box contains
void of air - in other words - vacuum.
The wooden box is now accelerated by a rocket with 9.81 meters for each second square in the space. That is the same acceleration due to gravity, which exists on earth. The box contains a small hole at the side panel, into which sunlight breaks in.
The beam penetrates through the hole into the box and hits on the other side of the panel and withdraws again from the crate. While
the light flows from one side to the other side of the panel, the box continues
to move on its own rate (pushed by the rocket). Thus, the light-beam changes
its direction; it is the difference between measurements
. .: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. Case 1:
Situation:
The box is not accelerated by the rocket - the box is weightless in space.
The light beam penetrates into the hole; the box does not move, since no
acceleration is available, therefore the light beam ist not shifted in
this case. The beam penetrates the hole into the box at point "E" and reach
point "F" on the opposite wall. Without acceleration by the rocket the
measurement "A" and "B"
. .: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. Case 2: 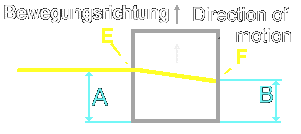
Case 2: Situation: The box is in the status after accelerated by the rocket and floats now with even rate there. The light beam penetrates into the hole, the box moves forward in even rate and the light beam reach the other side of the panel, this time shifted in its position through the acceleration of the rocket. The beam penetrates the hole in the box at point "E" and reach point "F" un the opposite wall. This light curvature is for an observer only within the box noticeable, only for those, who are subjected also to the acceleration of the rocket. For an observer, who is found to be outside the box, the light curvature is not available, since the beam flows is an straight path.
The
invasion of the light beam is seen subjective from the box, i.e. the box
is fixed steadily by the observer and the movement of the box is not perceived.
The
box is namely moving, but the light beam remains on its previous position
and moves only in its direction.
.
.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
_.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:.
Case 3 Case 3:
Situation: The box is constantly further accelerated by the rocket and flys with constantly increasing speed in the space. The light beam falls into the hole. The box continues to moves on and the light reach the other side of the panel, shifted from its position through the acceleration. The beam penetrates the hole into thr box at point "E" and reach the opposite side at point "F". Then the beam leaves the box. The boc still moves on, but the light beam remains on its previous course and moves only in its direction. We see subjectively from the light beam - this means that we are observing only the light beam. On the other way round, we would fix the crate (see case 2). Here
in the case 3, the beam make back a hyperbola - thus a curve. This is the
result of additional acceleration and the rising speed. The observer outside
the box sees the light beam however moving further in a straight line without
changing its position.
. .: * ~ *:. _.:
* ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.: * ~ *:. _.:
* ~ *:.
To
the diagram beam deflection:
The shortest connection between 2 points in curved space is the curve. Even this is a sign, that comets are also found to be moving on the shortest way (an elliptical course) since they move outside the solar system and are able to move back to the sun. The gravitation curves the space and the space brings the matter in motion. Curvature is actually defined as straight line bend to a curvature (an ellipse). Thit is the shortest way around a sun in a curved space. Planets also take elliptical course. Course
curvatures
Stephen Hawking and Black Holes Stephen
Hawking determines:
The
question of the contraction
One question and two different answers: The question is : Why is our universe found to be in the expansion phase and not in that of contraction. Professor Stephen Hawking answered hereby (readable in his book "A short history of the time 1988/2001" page 195: "This question can be answered with the weakest anthropic principle. The conditions in the contraction phase would not be suitable for the existence of intelligent natures, who could ask, why does the disorder increases in the same time-direction, in which the universe expands " Normal answer: " Since Hubble, we found out through measurements and observations in our surrounding universe that the universe expands at present and does not contract." Why is everything theorized and represented pedantically and accessed with the left hand to the right ear, when seizable observation results are available? It
is intentionally made complicated, so that not all can understand it.
SUMMARY - light-beam curvature (bend):
2) A light-beam curvature (bend) is caused by the gravitation. Both are correct.
Background
information
..:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:._.:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:._.:*~*:..:*~*:.
..:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:._.:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:._.:*~*:..:*~*:.
Stephen
Hawking and black holes
Hawking
determined: The time is pear-shaped - he means that a Big Bang took place
and that the time finds an end, and the relativity theory does not have
a global validity anymore in the black holes. Hawking means, that the beginning
of the universe must be determined by the same laws, which are valid at
all other times. He would have already approached his aim. He means, a
law is no law, if it is only effective some times. Referring to Einstein,
he said that one cannot curve the space, without including the time. space
and time are indissolubly connected to each other. The time seems to go
only in one direction.
..:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:._.:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:._.:*~*:..:*~*:.
Author: Robert Kinkel on 2002.4.4 after Christ Translation: German to English Tara Kinkel -on 2003.7.7. after Christ
|
|
|
|
.:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:. IMPRINT.:*~*:.:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:. ..:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:. .:*~*:..:*~*:..:* ~ .:*http://www.cybertaro.de.:*.:*~*:. .:*~*:..:*~*:. .:*~*:..:*~*:..:*~*:.http://www.kinkel-bischem.de .:*_.:*~.:*~*:..:*~*:. .:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~ .:* .:**:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:._.:*~*:.
Email to webmasters@kinkel-bischem.de webmaster@kinkel bischem.de D-Frankfurt/M Website opens on 2005 Update 11.11.2006 |